Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Tsujimura, Norio; Kunugita, Naoki*; Nishida, Kazutaka*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Kato, Masahiro*; Okubo, Hideki*
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 99(4), p.604 - 619, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.69(Biology)In April 2011, the International Commission on Radiological Protection recommended reducing the occupational equivalent dose limit for the lens. Such a new occupational lens dose limit has thus far been implemented in many countries, and there are extensive discussions toward its regulatory implementation in other countries. In Japan, discussions in the Japan Health Physics Society (JHPS) began in April 2013 and in Radiation Council in July 2017, and the new occupational lens dose limit was implemented into regulation in April 2021. To share our experience, we have published a series of papers summarizing situations in Japan: the first paper based on information available by early 2017, and the second paper by early 2019. This paper (our third paper of this series) aims to review updated information available by mid-2022, such as regarding regulatory implementation of the new occupational lens dose limit, recent discussions by relevant ministries based on the opinion from the council, establishment process of safety and health management systems, the JHPS guidelines on lens dose monitoring and radiation safety, voluntary countermeasures of the licensees, development of lens dose calibration method, and recent studies on exposure of the lens in nuclear workers and biological effect on the lens.
Yoshizawa, Michio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 64(8), p.439 - 441, 2022/08
, 64(8), p.439 - 441, 2022/08
no abstracts in English
Furuta, Hiroshige*; Sato, Kaoru; Nishide, Akemi*; Kudo, Shinichi*; Saigusa, Shin*
Health Physics, 121(5), p.471 - 483, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Environmental Sciences)Low dose radiation induced "health effects" containing cancer risk for a Japanese radiation worker cohort is epidemiologically evaluated using the personal dose equivalent (Hp(10)). On the other hand, Hp(10) is not recommended for epidemiological evaluation of cancer risks, since the Hp(10) is widely used for radiological protection purposes. In addition, the cancer risk depends on organ doses rather than Hp(10). Thus, we developed a new method for estimating organ doses from Hp(10) of radiation workers. The developed method enables epidemiological analysis against Japanese radiation workers by considering the response characteristics of personal dosimeters, exposure geometry and energy, and body size of radiation workers in Japan. In the future, we will reconstruct organ dose conversion factor and will evaluate the risk of cancer mortality and morbidity using the organ dose in Japan.
Manabe, Kentaro; Koyama, Shuji*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(4), p.489 - 496, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Environmental Sciences)It is important for radiation protection in diagnostic nuclear medicine to estimate organ absorbed doses in consideration of person-specific parameters. This study proposes a straightforward method for estimating organ doses which reflect an individual organ masses by scaling the reference doses based on the reference human models using the inverse ratio of the individual masses to the reference organ masses. The method was tested for the administration cases of  Tc-labelled colloids and
Tc-labelled colloids and 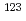 I-labelled sodium iodine to confirm the effectiveness of the method. The discrepancies of the doses estimated by the method were sufficiently small in terms of solid organs.
I-labelled sodium iodine to confirm the effectiveness of the method. The discrepancies of the doses estimated by the method were sufficiently small in terms of solid organs.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Momose, Takumaro
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 11, p.070008_1 - 070008_6, 2016/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency; National Institute of Radiological Sciences*
JAEA-Review 2015-007, 50 Pages, 2015/10
The review of the evacuation area due to the accident of TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station has completed and the deregulation has begun in some regions. The authors started this research in order to contribute to the understanding of individual dose that is assumed after the return of the residents. Measurements and evaluation using personal dosemeters were conducted at the typical living locations in the area where the evacuation orders are ready to be lifted and the residence restriction area. So the relationship between air dose and personal dose equivalent there was demonstrated observationally and experimentally. In addition, the estimation of the residents' individual doses in the pattern of their social lives expected after returning home.
Yamamoto, Hideaki; Yoshizawa, Michio; Murakami, Hiroyuki; Momose, Takumaro*; Tsujimura, Norio*; Kanai, Katsuta*; Cruz-Suarez, R.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 125(1-4), p.88 - 92, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)The purpose of this paper is to discuss the results of the third intercomparison exercise of external radiation dosimetry organized under the Regional Cooperative Agreement (RCA) in the East Asia region of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Twenty five laboratories from 16 member states participated in the exercise. Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) arranged the standard irradiation of the participants' dosimeters. The results of the measurements of the irradiated dosimeters for the determination of external doses were satisfactory for all participants, demonstrating good performance in their external dosimetry.
Uchida, Yoshiaki*; Saegusa, Jun; Kajimoto, Yoichi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Shimizu, Shigeru; Yoshizawa, Michio
JAERI-Tech 2005-012, 31 Pages, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Saegusa, Jun; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yoshizawa, Michio
Proceedings of 11th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-11) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/05
Relationships between dosemeter readings and the true dose equivalents at various workplaces were analyzed. From the analysis, it was shown that depending on the types of dosemeters, there exist a suitable calibration field, and the field differs by the difference of response characteristics of dosemeters. For the precise estimation of dose equivalent, it is important that measurement is carried out under the careful considerations of the difference between neutron spectrum at workplace and at calibration field, as well as the improvement of response characteristics of the dosemeters.
Saegusa, Jun; Yoshizawa, Michio; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yoshida, Makoto
Radioisotopes, 51(1), p.26 - 33, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Dung, N. P.; Murayama, Takashi; Otsuji, Katsuhiro*; Obata, Kazuichi; Murakami, Hiroyuki
JAERI-Tech 2001-047, 28 Pages, 2001/07
no abstracts in English
Sudo, Norimichi*; Kobayashi, Ikuo*; Murakami, Hiroyuki
Hoken Butsuri, 36(1), p.95 - 100, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Akifumi*; Ito, Masashi
JAERI-Tech 2000-089, 30 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Murakami, Hiroyuki
Isotope News, (558), p.57 - 60, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Tsujimura, Norio; Shinohara, Kunihiko; Momose, Takumaro
PNC TN8510 98-001, 13 Pages, 1998/07
None
Tsujimura, Norio; Shinohara, Kunihiko; Momose, Takumaro
PNC TN8410 98-083, 20 Pages, 1998/05
None
Murakami, Hiroyuki
Genshiryoku eye, 45(3), p.61 - 63, 1998/03
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Yoshizawa, Michio; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
Radioisotopes, 47(1), p.29 - 33, 1998/01
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Takenori
Hoken Butsuri, 33(2), p.121 - 142, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Tsujimura, Norio; Shinohara, Kunihiko; Momose, Takumaro
PNC TN8410 97-207, 25 Pages, 1997/06
None